TN 5.17 Post Installation Testing of SaniTite HP
Filename:
TN 5.17 Post Installation Testing of SaniTite HP.pdf
This document is the TN 5.17 Post Installation Testing of SaniTite HP. Deflection & Joint testing with table discussed.
Sanitary sewer is often tested after or during installation to ensure a sound installation was accomplished. Types of post installation field testing include deflection testing and joint testing. Specific testing required for the project will be found in the project specifications.
This technical note is not meant to supersede any project specification, but should be used in conjunction with the project specification and national testing standards as it relates specifically to SaniTite HP pipe.
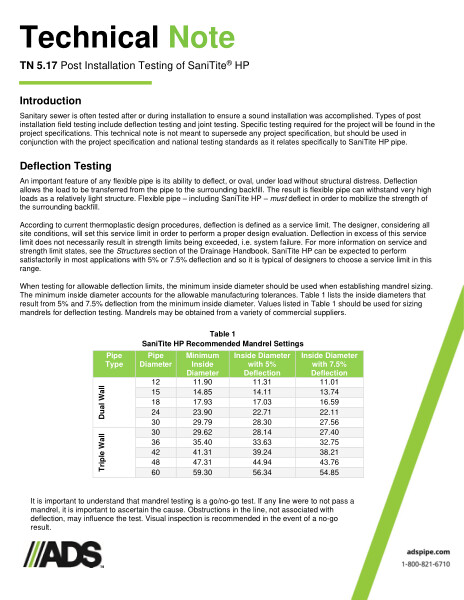
An important feature of any flexible pipe is its ability to deflect, or oval, under load without structural distress. Deflection allows the load to be transferred from the pipe to the surrounding backfill. The result is flexible pipe can withstand very high loads as a relatively light structure. Table 1 shows the values for SaniTite HP Recommended Mandrel Settings.
Joint testing is an important part of any sanitary sewer system, both in testing for infiltration and exfiltration. Infiltration aids to estimate the amount of sewer water that will be conveyed to, and ultimately treated by, the waste water treatment plant. Exfiltration aids to estimate the loss of sewage water into the surrounding soil. The two primary ways of testing sewer pipe joints for infiltration and/or exfiltration is using air or water to create a constant pressure within the system. Table 2 shows the values for Time to Pressure Drop for SaniTite HP.
Testing sanitary sewer joints via water infiltration or exfiltration is a common practice. For SaniTite HP, this testing should be conducted in accordance with ASTM F2487. These standards entail first observing the ground water conditions and, if applicable, measuring the infiltration rate of the ground water through the joints. If ground water is not applicable, then the line is filled with water and the leakage is observed through exfiltration.
For the infiltration test the ground water must be at least 2 feet above the crown of the pipe for the entire test section. If this groundwater condition is not present, exfiltration testing should be used. Allowable leakage rate noted.
